42 hf molecular orbital diagram
MO diagram of HF and HCl with explanation (Heteronuclear ... This lecture clearly explains the molecular orbital diagram of heteronuclear diatomic molecule (HF & HCl). This will help students of H.S., BS-MS, B. Sc., M.... What are nonbonding molecular orbitals? + Example 13.4.2014 · A non-bonding orbital (NBMO) is a molecular orbital for which the addition or removal of an electron does not change the energy of the molecule. Molecular orbitals come from the linear combination of atomic orbitals. In a simple diatomic molecule such as HF, F has more electrons than H. The s orbital of H can overlap with the 2p_z orbital of fluorine to form a …
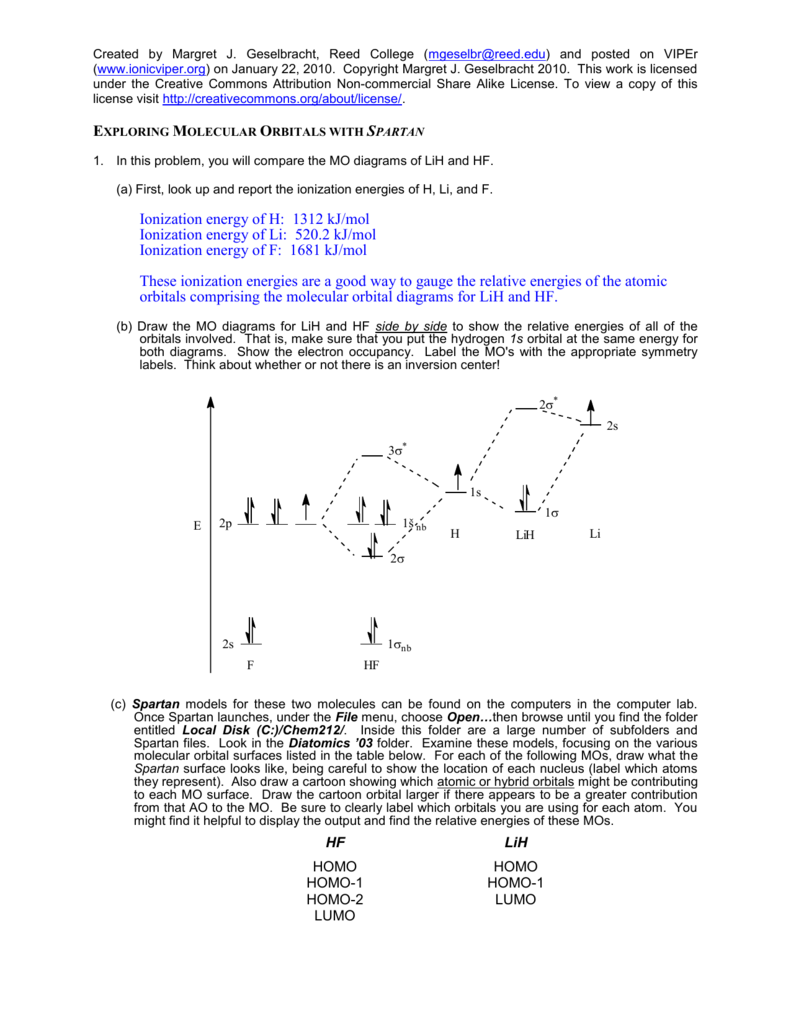
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih - schematron.org Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.
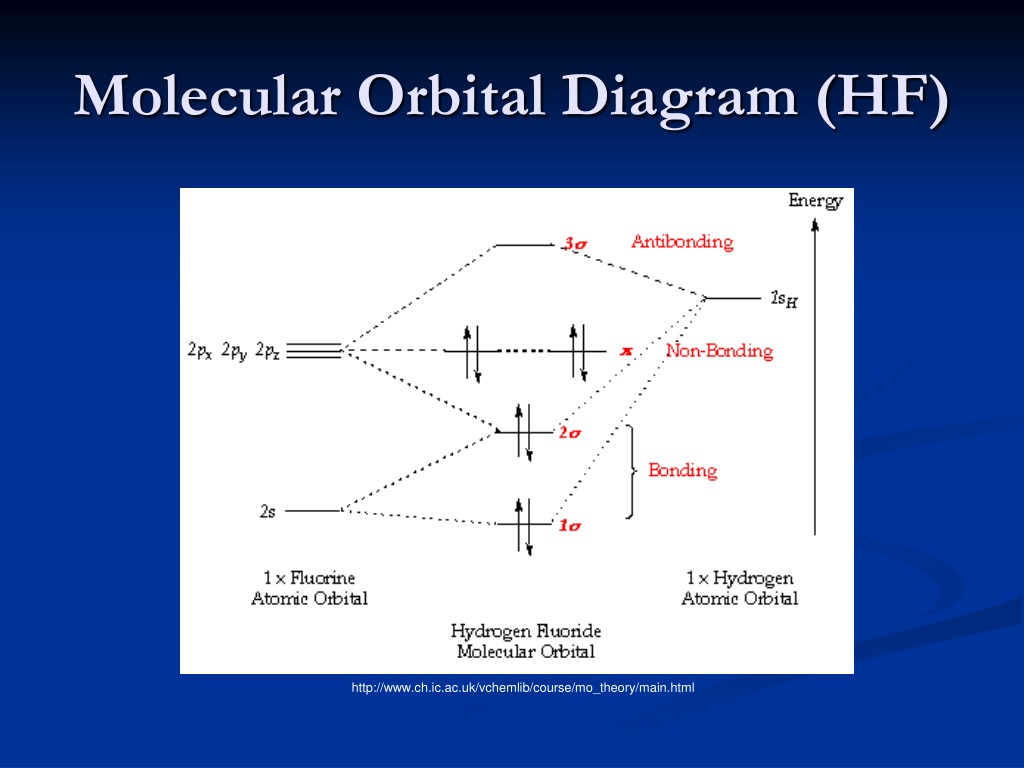
Hf molecular orbital diagram
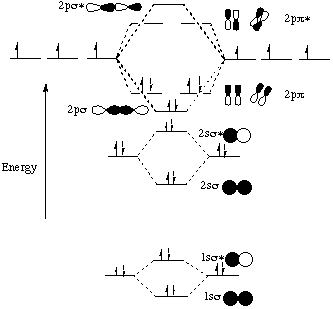
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride - ChemTube3D Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 ... - BYJUS NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” is the fourth chapter of the term – I CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus for session 2021-22. This chapter touches on several fundamental concepts in the field of Chemistry (such as hybridization and the modern theories on chemical …
Hf molecular orbital diagram. 182: Semi-empirical Molecular Orbital Calculation on HF ... 182: Semi-empirical Molecular Orbital Calculation on HF. Calculate the wavefunctions and energies of the σ orbitals in the HF molecule, taking β = -1.0 eV. The values of the Coulomb integrals αH and αF are taken as the negatives of the orbital ionization energies of the atoms. The molecular orbital is formed as a linear combination of the ... › definition-of-molecular-weightWhat Is Molecular Weight? Chemistry Definition Jul 03, 2019 · Molecular Weight Versus Molecular Mass . Molecular weight is often used interchangeably with molecular mass in chemistry, although technically there is a difference between the two. Molecular mass is a measure of mass and molecular weight is a measure of force acting on the molecular mass. A more correct term for both molecular weight and ... Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. | Download ... Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ... MO of HF.mpg - YouTube An advanced molecular orbital diagram of HF for the inorganic or physical chemistry student.
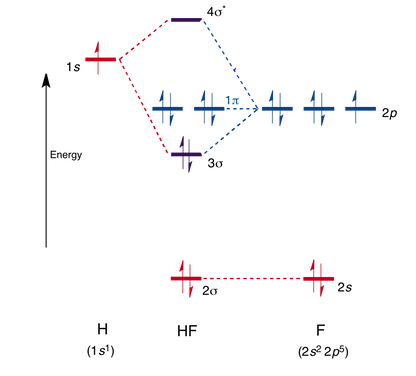
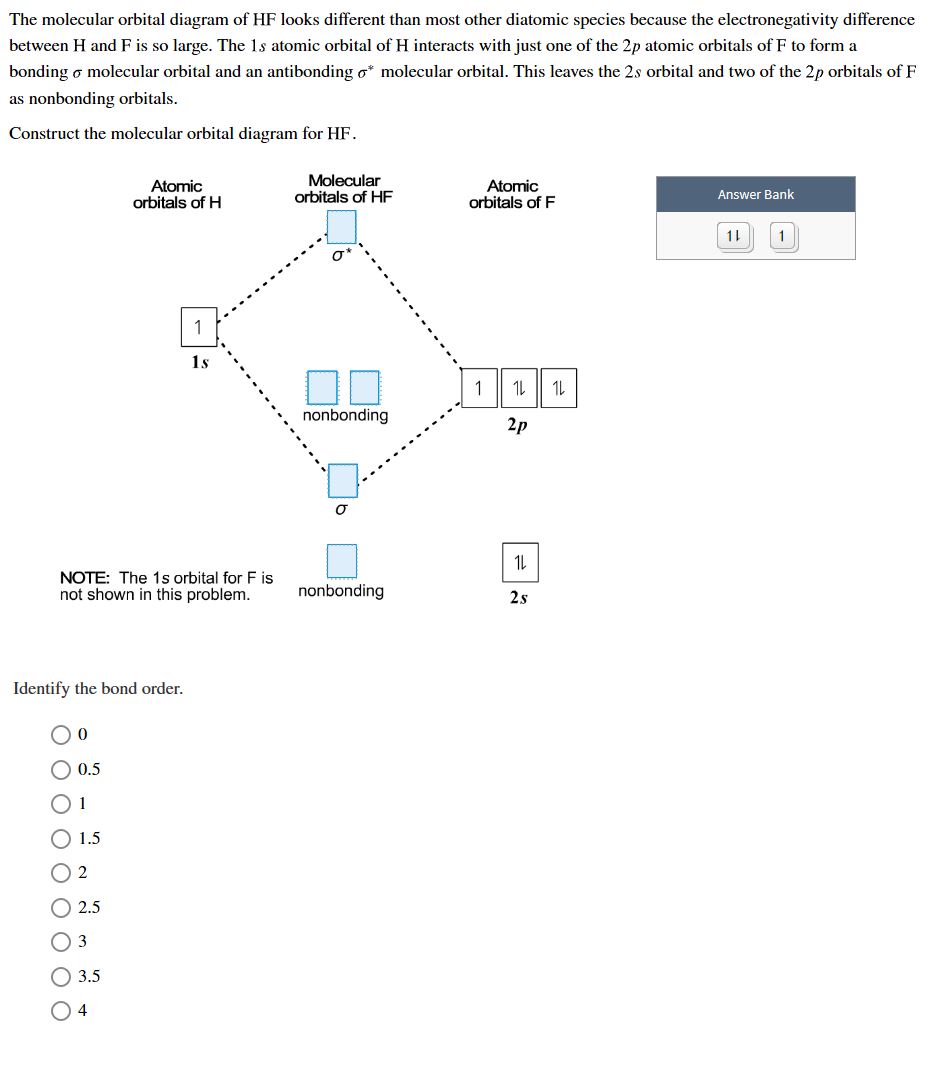
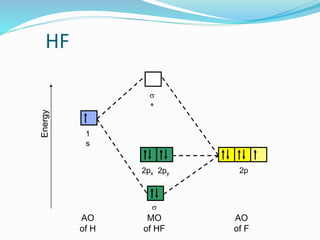
BrF3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... 25.2.2022 · Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular Orbital Theory, which is used to sketch the MO diagram of any given molecule, is a complex yet important concept of chemical bonding. In quantum mechanics, MO theory deals with spatial and energetic properties of electrons and talks about the LCAO (Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals) to form MO( Molecular Orbitals). Molecular orbital - Wikipedia In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one … A.2. Example: heterodiatomic molecule HF - Chemistry ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves). (Get Answer) - The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks ... The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of Hinteracts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding a molecular orbital and an antibonding o* molecular orbital.
MolecularOrbitals - Maple Help - Waterloo Maple Figure 1: LCAO MO Diagram for HF (Author: LeeAnn Sager. Used with permission.) The purpose of this activity is to use Hartree-Fock self-consistent-field approach to calculate the molecular orbitals of HF in the minimal atomic basis (STO-3G) and to compare the molecular orbitals to the qualitative LCAO approach. topblogtenz.com › cyanide-cn-lewis-structureCN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond order Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. ap chem semester 1 MCQs Flashcards & Practice Test - Quizlet Start studying ap chem semester 1 MCQs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Hbr Mo Diagram - Diagram World Molecular orbitals of HF. Draw the MO diagram for HBr including energy levels each orbitals shape each orbitals character meaning what atomic orbitals contribute to each MO. H1 is bonded in a linear geometry to two equivalent Br1- atoms. And how much symmetry labels eg. And how much symmetry labels eg.
J-coupling - Wikipedia In nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, J-couplings (also called spin-spin coupling or indirect dipole–dipole coupling) are mediated through chemical bonds connecting two spins. It is an indirect interaction between two nuclear spins that arises from hyperfine interactions between the nuclei and local electrons. In NMR spectroscopy, J-coupling contains information about …
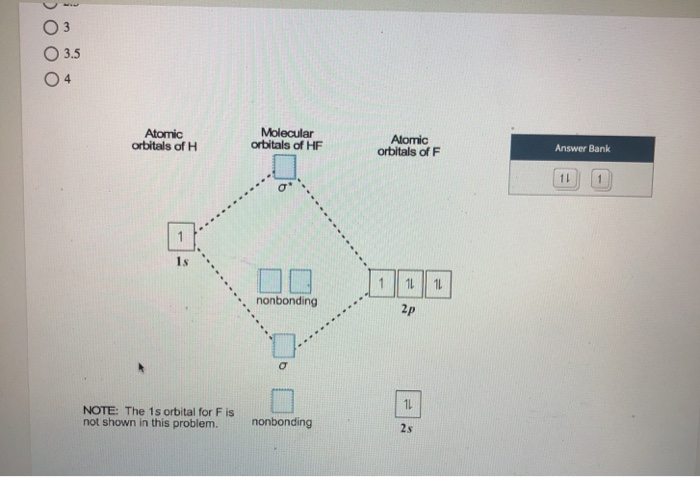
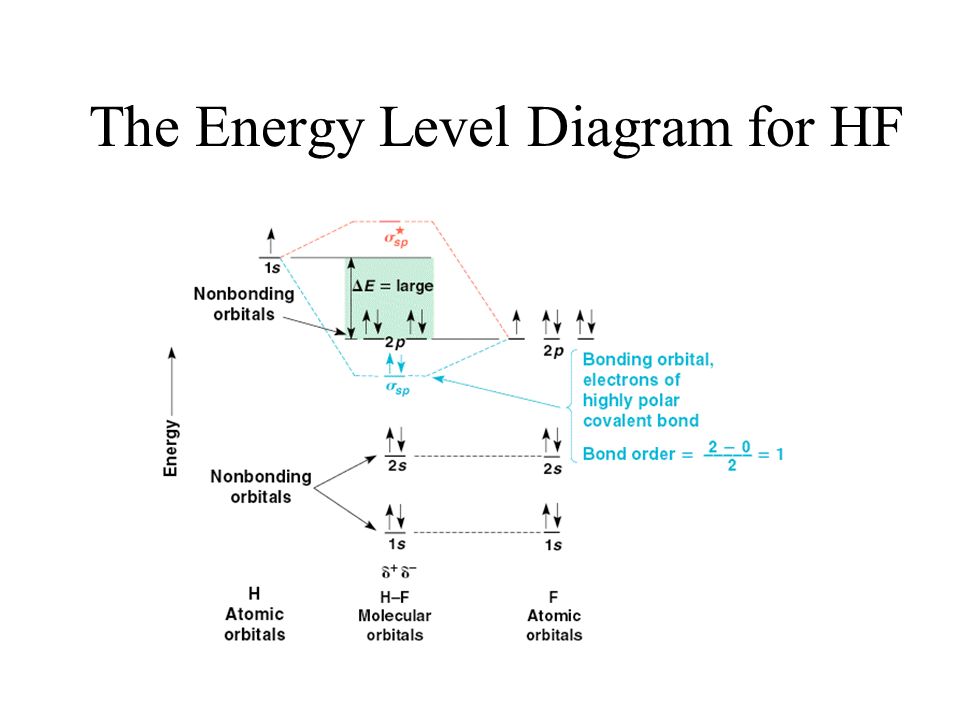
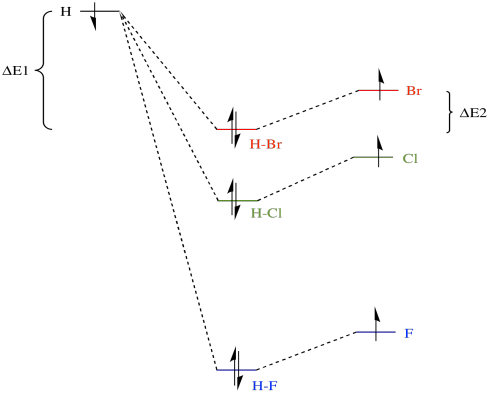
Solved Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use ... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for HF. Use only the valence electrons for your diagram. The 2s orbital of F atom has an energy more than 26 eV lower than that of the H 1s, so there is very little interaction between them. The F 2p orbital (-18.65 eV) and the H 1s (-13.61 eV), on the other hand, have similar energies, allowing them to
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Answered: "he molecular orbital diagram of HF… | bartleby The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o* molecular orbital.
Solved The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different ... The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
HF - uwosh.edu HF HOMO Orbital The HOMO orbital is the highest energy molecular orbital occupied by electrons. In HF, the HOMO orbitals are the double degenerate pi 2px and 2py and pi orbitals. To get a 3-D model you can manipulate, click here. Download time may be significant the first time the applet is loaded. HF LUMO Orbital
Understanding FHF- molecular orbital diagram? I need help understanding the molecule FHF-'s molecular orbital diagram: So I know that "a g" refers to the 2p z and 2s orbitals of fluorine atoms ... Why HF is said to be formed from H-1s and F-2pz overlap? 2. Energy level of hybrid orbitals in the molecular orbital energy diagram. 0.
Constructing the HF molecular orbital energy level diagram ... In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Molecular_orbital_diagramMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Which is the molecular orbital diagram for HF? - Quora Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
Answered: The molecular orbital diagram of HF… | bartleby The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding o molecular orbital and an antibonding o molecular orbital.
Tutorial: Display of Orbitals and Molecular Surfaces Tutorial: Display of Orbitals and Molecular Surfaces. 3. Natural Molecular Orbital Analysis. The occupied canonical orbitals that are obtained from a Hartree-Fock (HF) calculation are generally delocalized. In many situations, this is undesirable because it is difficult to attach a chemical interpretation to these molecular orbitals.
Molecular Orbitals of Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) - Chemistry ... This source states that the three s-orbitals of hydrogen and fluorine interact to form three new molecular orbitals, while other sources say that the 2s orbital is non-bonding. ... {HF}$ one can construct MOs using the $1s$ AO on H and the $2s$ and $2p$ AOs on F. In general, the contribution to MOs is determined by the coefficients in the ...
Module Two Chem 101 Problems Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Module Two Chem 101 Problems. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
› ~lawm › Ch 5 SolutionsMiessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy molecular orbital with respect to the 3s orbital of sulfur. This lowest energy orbital is essentially nonbonding.
MO for HF - Chemistry LibreTexts Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
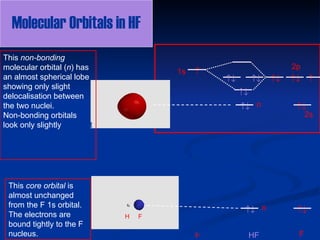
Slides22d - Carnegie Mellon University Illustrating molecular orbitals (valence electrons only) in HF whose atoms are very different in electronegativity. The lowest molecular orbital is virtually indistinguishable from the 2s atomic orbital on F (because of the large energy difference with H's atomic orbital).
(Get Answer) - The molecule HF has a single bond between H ... The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The 1s atomic orbital of Hinteracts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a...
(PDF) Inorganic Chemistry Housecroft | Yurika Almanda ... Pembuatan Senyawa kompleks asetial asetanoat. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 ... Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure solved by expert teachers from latest edition books and as per NCERT (CBSE) guidelines.Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks.
Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
PDF Introduction to Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory Hartree-Fock Molecular Orbital Theory 1. Invoke the Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Express the electronic wavefunction as a single Slater Determinant 3. Solve for those orbitals which minimize the electronic energy (variational method) This winds up being mathematically equivalent to assuming each electron interacts only with the average
PDF Calculating the Energies of Molecular Orbitals much of each atomic coefficient is required to make each of the molecular orbitals. The coefficients for the highest energy MO wavefunction is solved below. Repeat these calculations for determining the coefficients of this molecular orbital, but then go on to calculate the coefficients for the other two MO's in our HF molecule.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 ... - BYJUS NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure” is the fourth chapter of the term – I CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus for session 2021-22. This chapter touches on several fundamental concepts in the field of Chemistry (such as hybridization and the modern theories on chemical …
Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride - ChemTube3D Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. CONTROLS . Click on the HF molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in


















Comments
Post a Comment