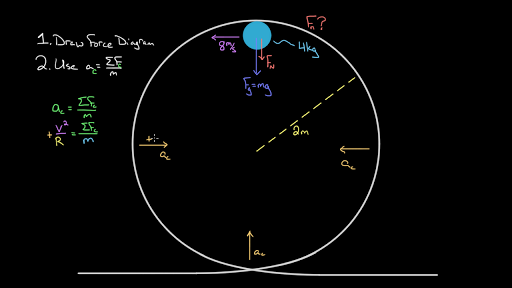
38 free body diagram roller coaster
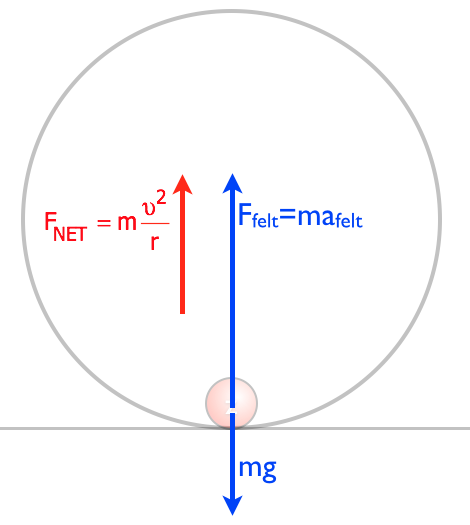
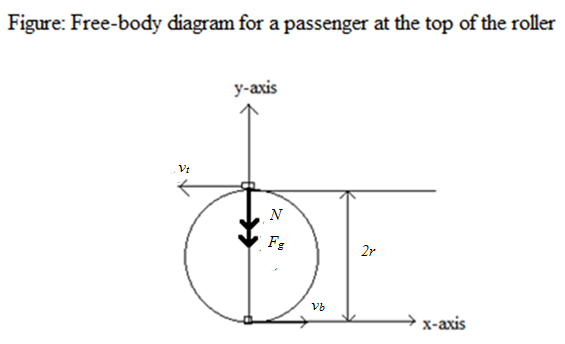
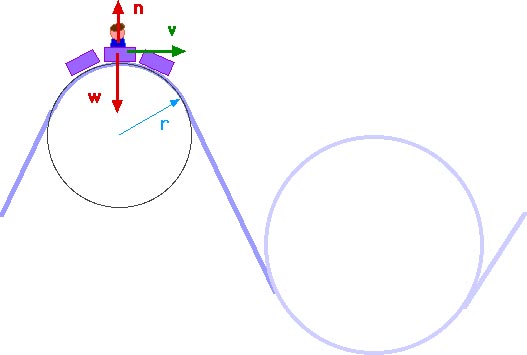
Dec 28, 2019 · See the free-body diagram in attachment. There are only two forces acting on the roller coaster at the top of the loop: The weight of the roller coaster, acting downward, indicated by (where m is the mass of the roller coaster and g is the acceleration of gravity) The normal reaction exerted by the track on the roller coaster, acting downward, and indicated with N Dec 26, 2018 · Roller coaster rides are notorious for creating accelerations and g-forces which are depicts the free-body diagrams for a rider at four locations along the loop. hello, i'm trying to study for the mcat, and I have a conceptual question about normal force, mg, and centripetal force during a loop-de-loop on a.At every point on a roller coaster ride, gravity is pulling you straight down.
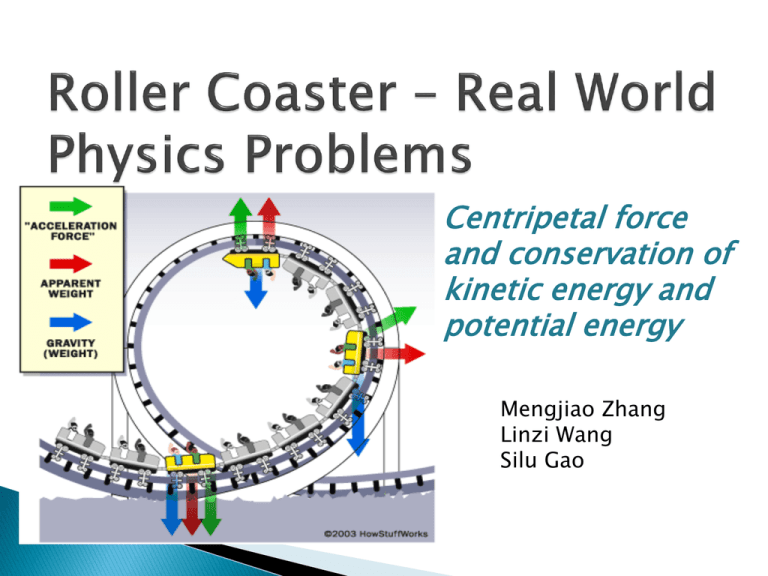
Anna Litical is riding on The Demon at Great America. Anna experiences a downwards acceleration of 15.0 m/s2at the top of the loop and an upwards acceleration of 20.0 m/s2at the bottom of the loop. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 1000 kg roller coaster car. Steps 1 and 2 involve the construction of a free body diagram and the identification of known and unknown quantities.

Free body diagram roller coaster
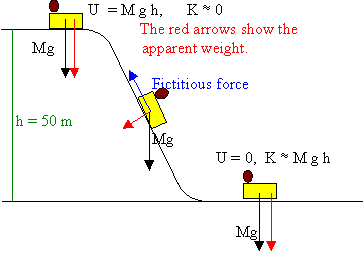
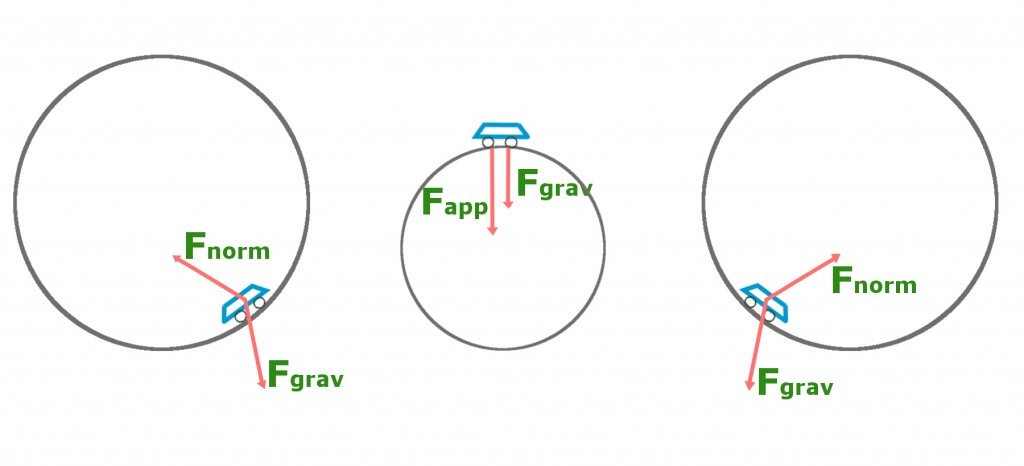
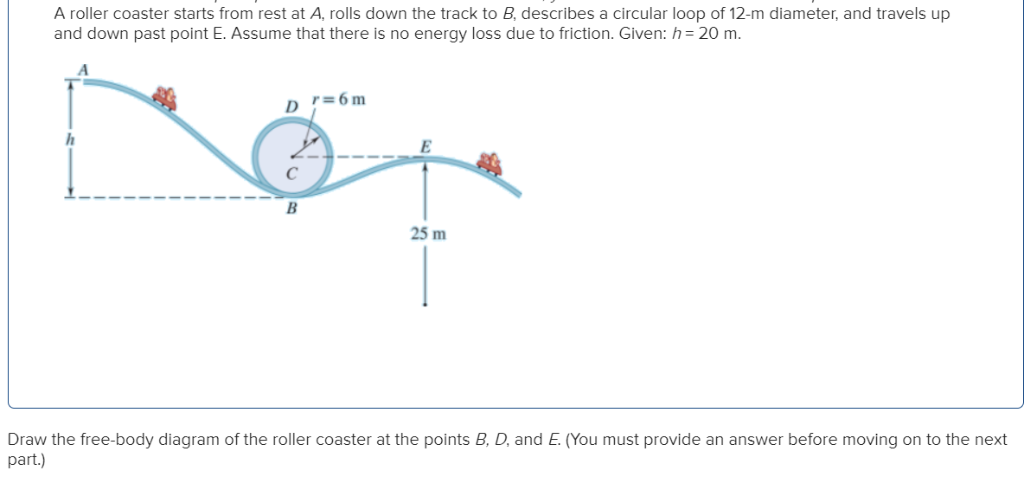
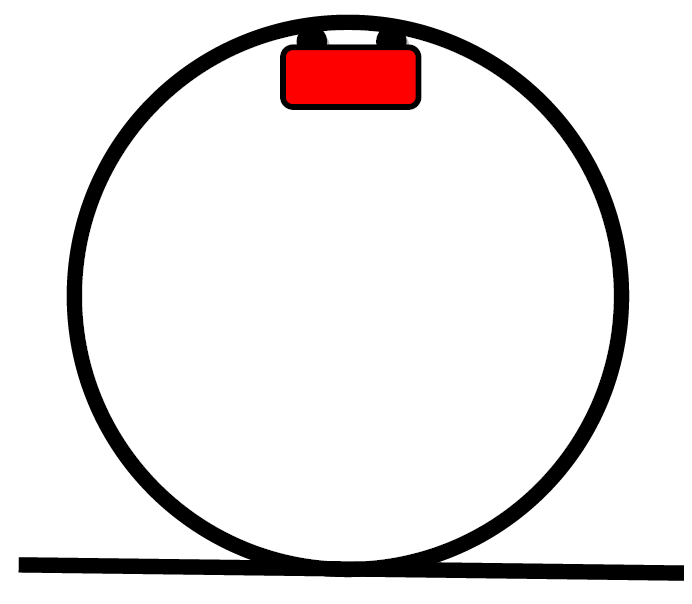
A roller coaster’s initial height and slope determines its length. The higher the initial point, the longer the path. It is best that the initial roller coaster slope not be steeper than ±2.5, otherwise the marble may slide instead of roll. This guideline is an outcome from testing different initial slopes. Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and ...
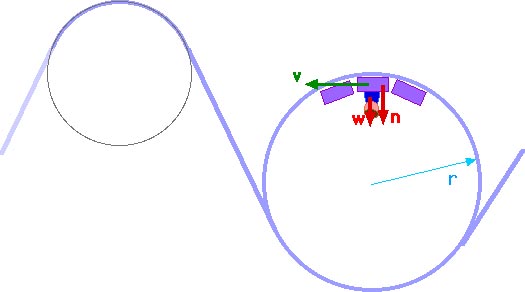
Free body diagram roller coaster. Physics Q&A Library Draw a free body diagram of the roller coaster car with all appropriate forces in three locations. At the bottom of the loop Halfway up the loop (or ¼ of the way around the entire thing) At the top of the loop Based only on your diagrams, where will the rider experience the greatest force? Mar 08, 2008 · i researched about free body diagrams and roller coasters. all i have now for the straight away is , f-gravity, f-normal, f - applied, and f- friction Other than when the coaster ( and passengers) are being pulled up the incline by a chain mechanism or other means, there is no applied force; otherwise you have correctly identified the other forces acting for the straightway. Q. In which free-body diagram are the forces correct on a roller coaster car when it is upside down at the top of the . loop-de loop? answer choices . alternatives . answer explanation . Tags: Topics: Question 9 . SURVEY . Ungraded . 30 seconds ... Nov 29, 2021 · Mentor. 45,204. 1,542. jsmith613 said: so we have a free body diagram looking like: Up: reaction force. down: mg, mv^2/r. Never put 'centripetal force' on a free body diagram. There are only 2 forces acting on the body: The weight, mg, and the force of the earth pushing up, the 'reaction force'. The Centripetal Force and Direction Change.
The two diagrams below depict the free-body diagram for a 1000-kg roller coaster on the first drop of two different roller coaster rides. Use the above principles of vector resolution to determine the net force and acceleration of the roller coaster cars. Assume a negligible effect of friction and air resistance. First, draw a free-body diagram and note that F grav = 490 N, down. Second, calculate acceleration by. a = v 2 / R = (16 m/s) 2 / (15 m) = 17.1 m/s/s, up. Then note that F net = m • a = 853 N, up (toward center). Now F grav supplies 490 N of downward force, so the F norm must overcome this down force and still supply the sufficient F net in the up direction. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg. The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the left of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed rightwards and ... Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster Draw the free body diagrams for a coaster at the boom and top of a loop and write the equaons for the net force. mg F net F N F net =ma = ma c The net force in the loop must be centripetal force F net = F N
A roller coaster’s initial height and slope determines its length. The higher the initial point, the longer the path. It is best that the initial roller coaster slope not be steeper than ±2.5, otherwise the marble may slide instead of roll. This guideline is an outcome from testing different initial slopes.

A 235 Kg Roller Coaster Reaches The Top Of The Steepest Hill With A Speed Of 5 60 Km H It Then Descends The Hill Which Is At An Angle Of 45 O And Is 45 0

A Roller Coaster Cart And Passenger Has A Capacity Of 2 000 Kg The Roller Coaster Needs To Be Designed Such That The Cart And Passengers Can Make It Around A Loop That













Comments
Post a Comment